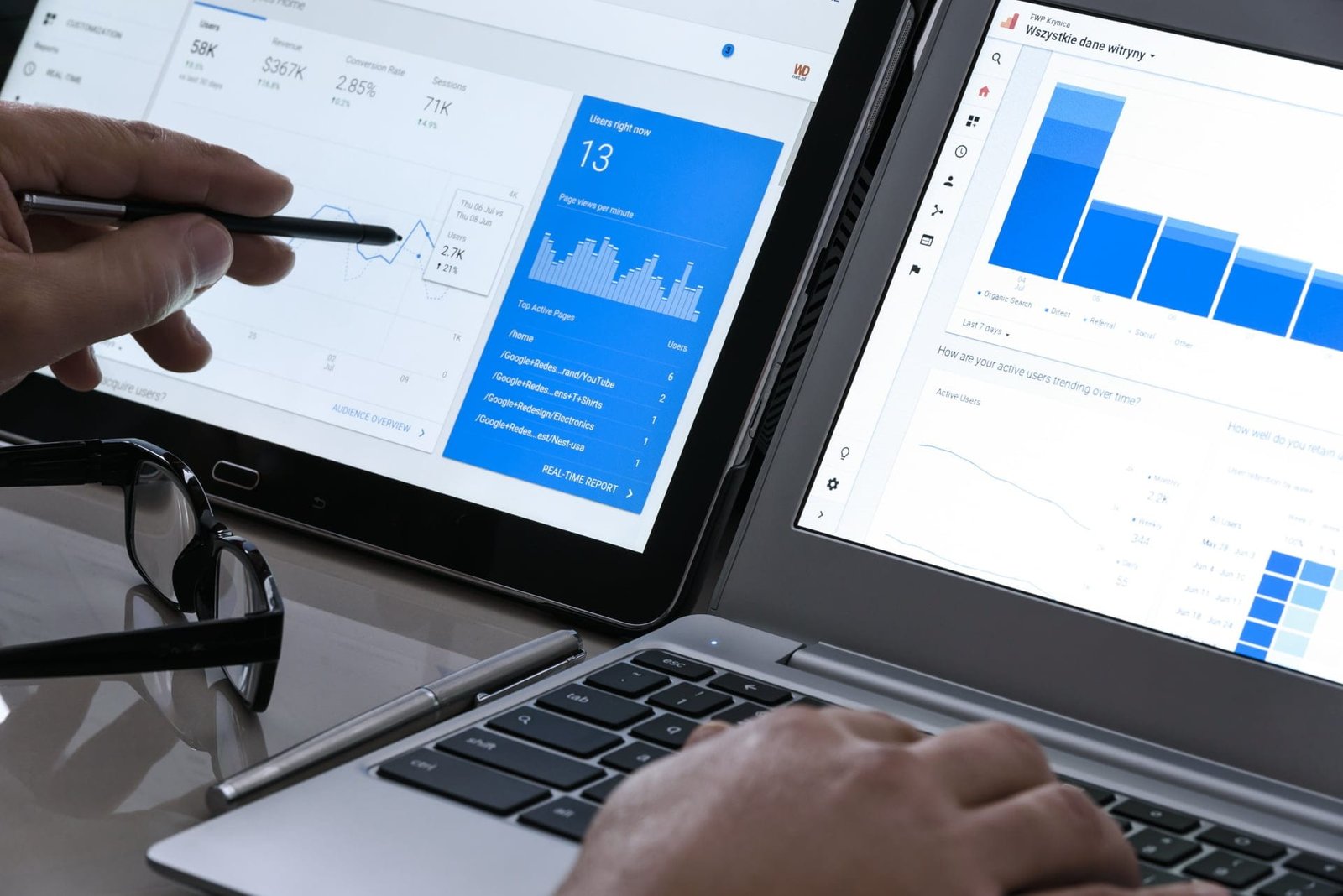
What is Google Analytics?
If you are wondering what Google Analytics does, it is basically a web analytics tool that should not be missing in your company if you want to analyze the results that your marketing strategy is having. This platform generates reports on the activity of our website as important as:
- What is my target audience?
- From where do they access my web site? (Origin of web traffic)
- How do they behave on my website?
- What is the conversion rate of the visits I receive?
Look at all the information that Google Analytics provides you with and transform it into tactics to achieve your goals.
How to configure Google Analytics?
If you are a beginner and still don’t know how Google Analytics works, here we will explain the first steps to start using this platform.
Paso 1. Crea una cuenta. Si todavía no has creado tu cuenta en Google Analytics, accede a google.com/analytics/ y elige “Comenzar gratis”. Si ya tienes una cuenta, inicia sesión en Analytics.
Step 1. Create an account. If you have not yet created your Google Analytics account, go to google.com/analytics/ and choose “Get started for free”. If you already have an account, log in to Analytics.

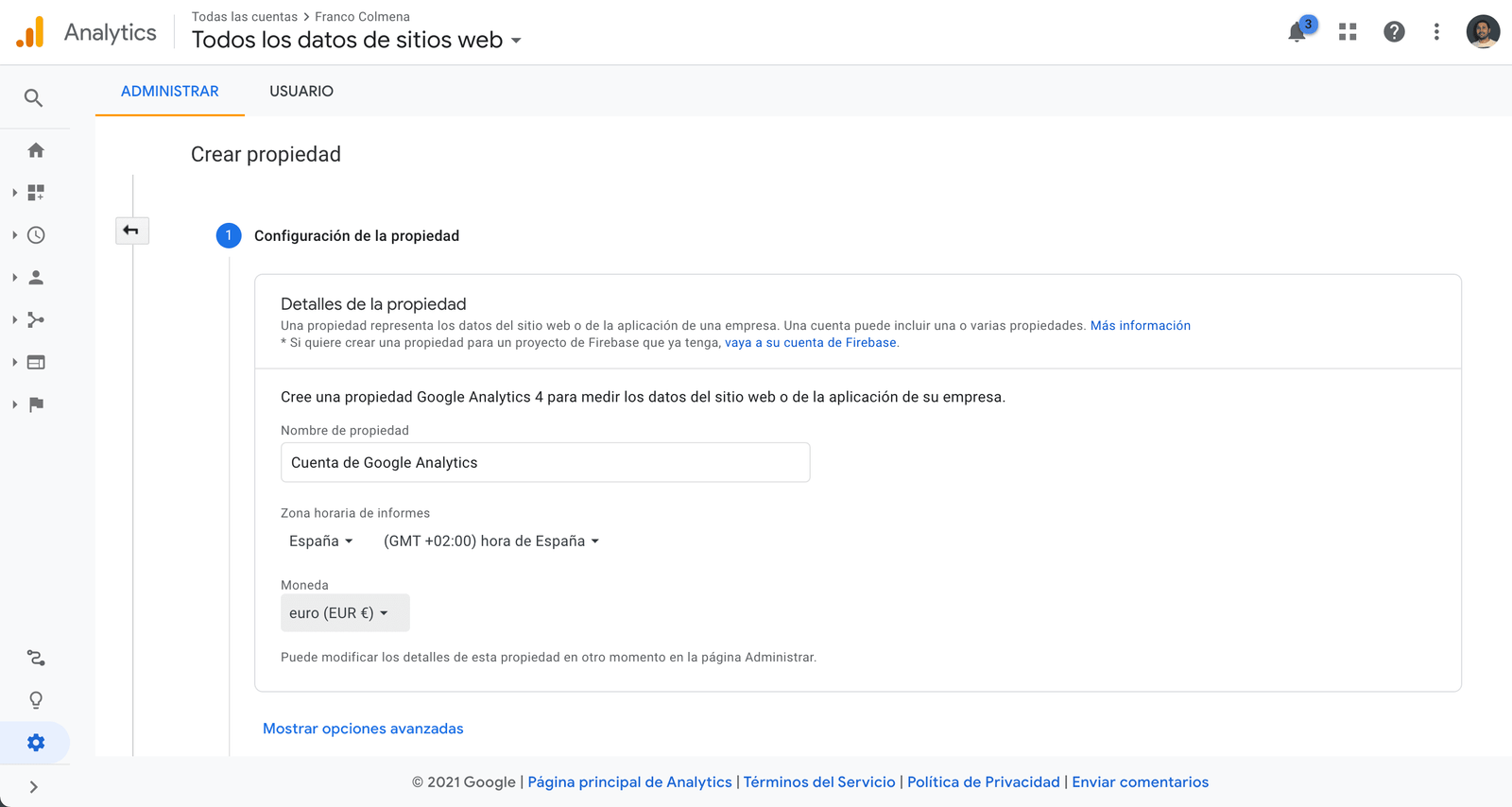
Step 2. Configure your website property. Analytics detects this property as a representation of your website that serves to collect all the data from it.

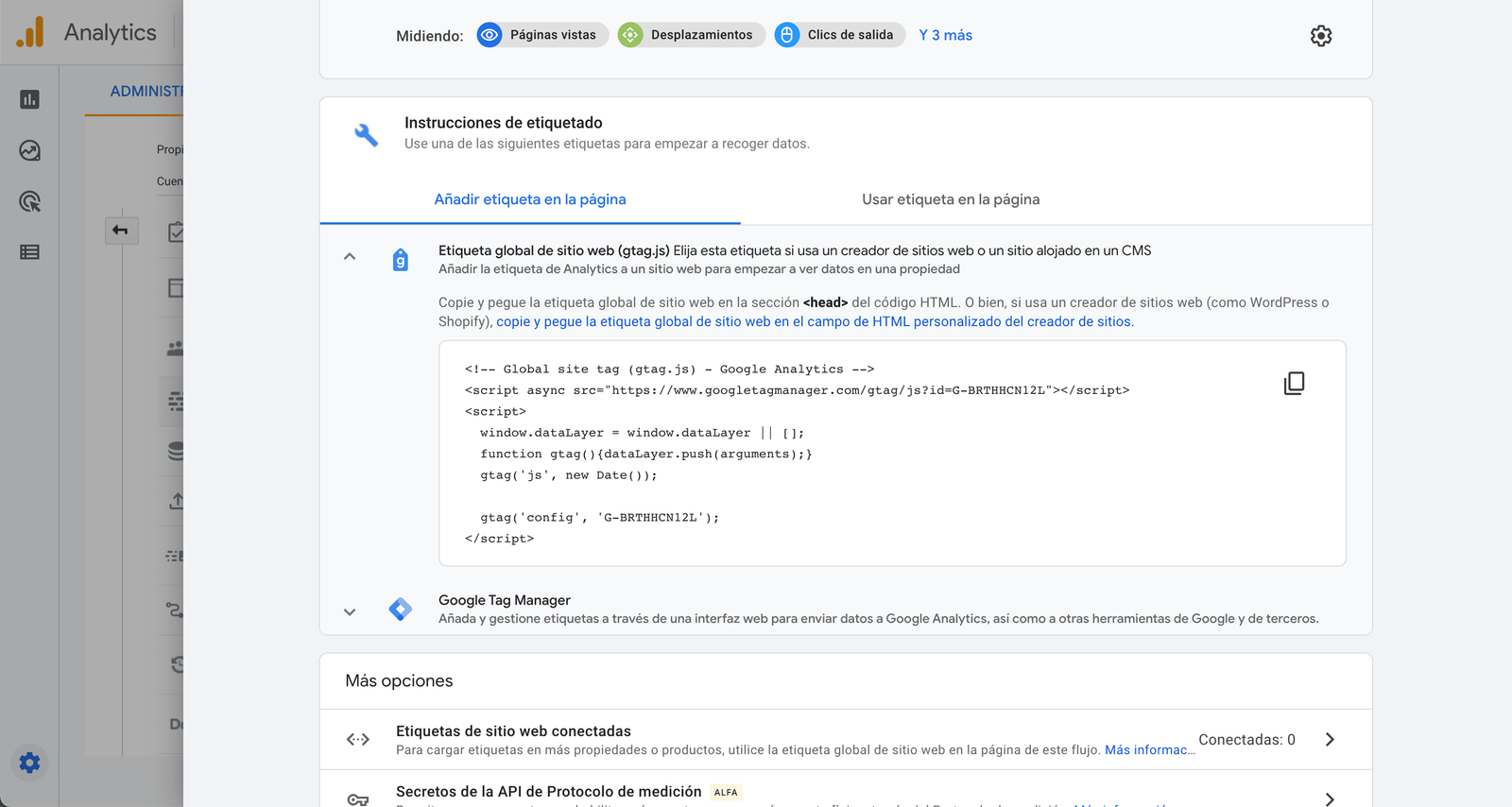
Step 3. Modify the tracking code. When you have created the property, it will generate a unique tracking ID and a global website tag that includes the corresponding tracking ID that you will have to insert in your web page, whether it is you, your web master or your marketing agency. Where to find the google analytics tracking code? Follow these steps: Manage > ACCOUNT > PROPERTY > Tracking information > Tracking code.

Step 4. Set up your account. Set your goals, configure dashboards, access custom reports, configure your properties and views. For example, you can link your Google Ads and Analytics accounts.
Understands reporting: Google Analytics metrics and data.
Once you have set up your Analytics account, you can start the analysis part. This tool will provide you with a great deal of information. Next, we will explain the basic metrics that you should know divided into 4 large blocks.
Visits
If you want to know who visits your website, go to Audience > Overview.
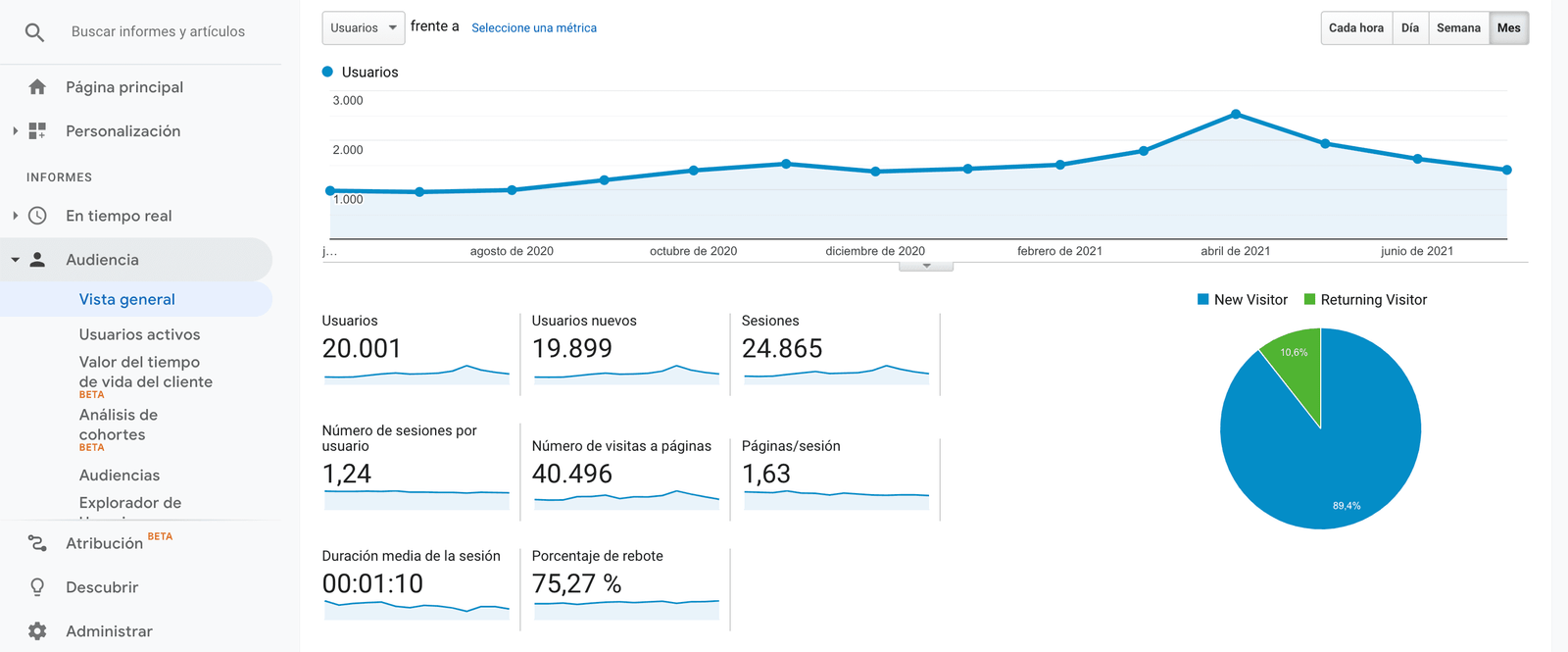

Important: Do not be fooled if you notice that you have a very high number of visits. This data alone does not give relevant information.
- Unique visitors. The same visitor can access your website several times and generate several visits. We are not interested in this. We want to know how many different users have accessed our site. This metric will tell you the percentage of new visitors (New Visitor) and visitors who have already entered your site before (Returning Visitor).
- Page views: How many times has a particular page of your website been opened? Maybe you have created an ad that takes the user to the landing page (for example). Find out if this page has been opened the most times (how many impressions it has had).
- Pages per visit. Here we obtain information about the navigation of a user. It tells us which pages you have visited. The more pages you visit, we understand that the more interest you will have.
- Average session duration or average time on the page. How long does a user stay on our website? This metric is highly valued by Google, since the search engine understands that the longer the time spent on our site, the higher its quality (because the user considers our content useful).
- Percentage or bounce rate: How many users have entered your website and left without taking any action? Ideally, this percentage should be as low as possible, which will indicate that we are offering a good browsing experience to the user.
- Average frequency of visits: How many days does it take from the time a user visits Average frequency of visits: How many days does it take from the time a user visits our website to the time he/she visits it again? to the time he/she visits it again?
Target audience
Find out who your buyer persona is. You may be targeting the wrong audience for your marketing efforts.
- Demographic data.
Audience > Demographics > Overview.
It is useful if we want to segment our audience by age or gender.
- Geographical data.
Audience > Geographic Information.
From which country does each user access the site? You may be more interested in segmenting your target audience based on language or location.
- Repeat visitors.
Audience > Behavior > New vs. returning customers.
We have already mentioned that we must distinguish between the New Visitor and the Returning Visitor. Ideally, as your website progresses over time, the number of returning visitors should increase.
- Technology.
Audience > Technology.
Where do users access my site from? Get information about the devices, operating system and browsers they use. For example, one result could be that most of your users access from Chrome, with mobile devices and Android operating system.
Origin of web traffic
Let’s see how users access our website and how they behave once they are inside.
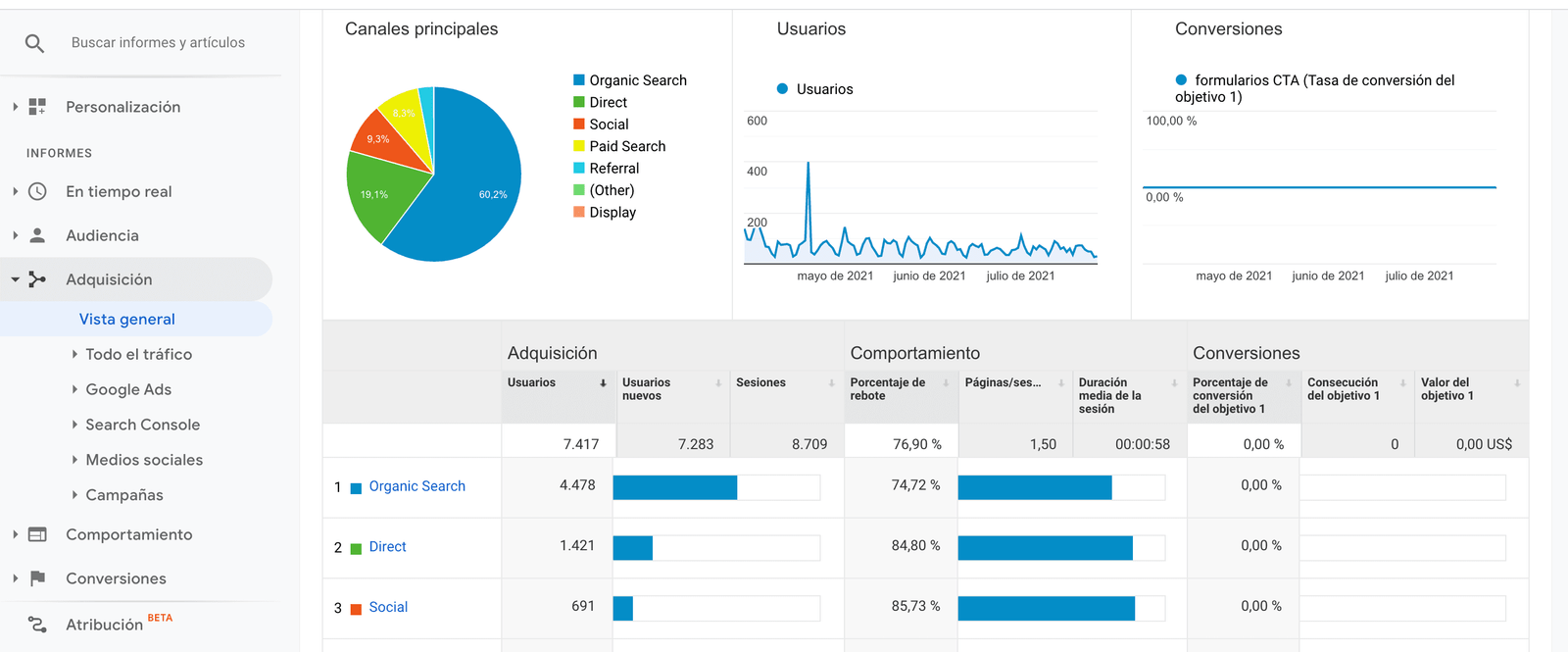

- Channels
Acquisition > All Traffic > Channels
That is, the traffic sources, from where are we receiving visits? The sources you will see are the following:
- Organic traffic. Visits that come from search engines such as Google, Bing or Yahoo.
- Direct traffic. Visits that directly enter the URL of our website in the browser.
- Social traffic. Traffic received through social networks.
- Referred traffic. They access from links to our content.
- Keywords
Keywords are those that users have entered in search engines and through which they have accessed our website. This metric is very important for our SEM or SEO positioning strategy.
For organic or SEO traffic: Acquisition > Search Console > Queries
- Search Engine Optimization
Link Analytics with Google Webmaster Tools. It will provide us with useful information such as impressions, CTR, number of clicks received…
Conversions
Google Analytics allows you to set four types of goals: destination, duration, pages per visit or events. You can configure these goals in the admin tab in the view column, “Create new goal”.
Ideally, you should define your goals and use Analytics to check if they are being met. It is useless to have many visits (potential customers) if your goal is to translate them into real customers.
- Destination. That is, users access your website from a specific URL. It is the page that attracts the visitor.
- Duration. Set the minimum time you want a visitor to stay on your website.
- Pages per visit. How users interact on your website.
- If you have included a call-to-action element (call to action) such as a video, it is interesting to discover the number of reproductions that the video has had.
How to measure these objectives?
Conversions > Objectives > Overview.
Here we will see how many objectives we have met and which ones in particular.
Conversions > E-commerce > Overview.
¿Qué valor tienes las conversiones? Es decir, el valor de la facturación en cada objetivo cumplido.
Conversions > Multichannel funnels > Overview.
Sales funnels are a very useful tool that allows us to follow the process that a user follows from the moment he/she is interested in our business (lead) until he/she becomes a real customer. Find out what a sales funnel is and how to implement it in our post: ? What is a sales funnel?
Conclusion
As you will have seen, there is no point in setting objectives and carrying out a marketing strategy if you do not analyze its effectiveness through results. Undoubtedly, Google Analytics is a simple web analytics tool that should not be missing in your business.