What is the Canvas model and how to do it step-by-step?
The Canvas model or “The Business Model Canvas” allows you to design your business model in a simple way and in just a few steps. Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur were in charge of developing it in the book Business Model Generation.
This tool simplifies the creation of your business model, first because it is very graphical (you can have a global view of your business) and second because it is summarized in 9 key elements: key partners, key activities, key resources, cost structure, revenue lines, channels, customer relationships, customer segments and value proposition.
This last aspect is arguably the most important, as it is at the center of the canvas (see image). The reason? Today what really makes you special and differentiates you in the marketplace is having a unique value proposition for your customers.
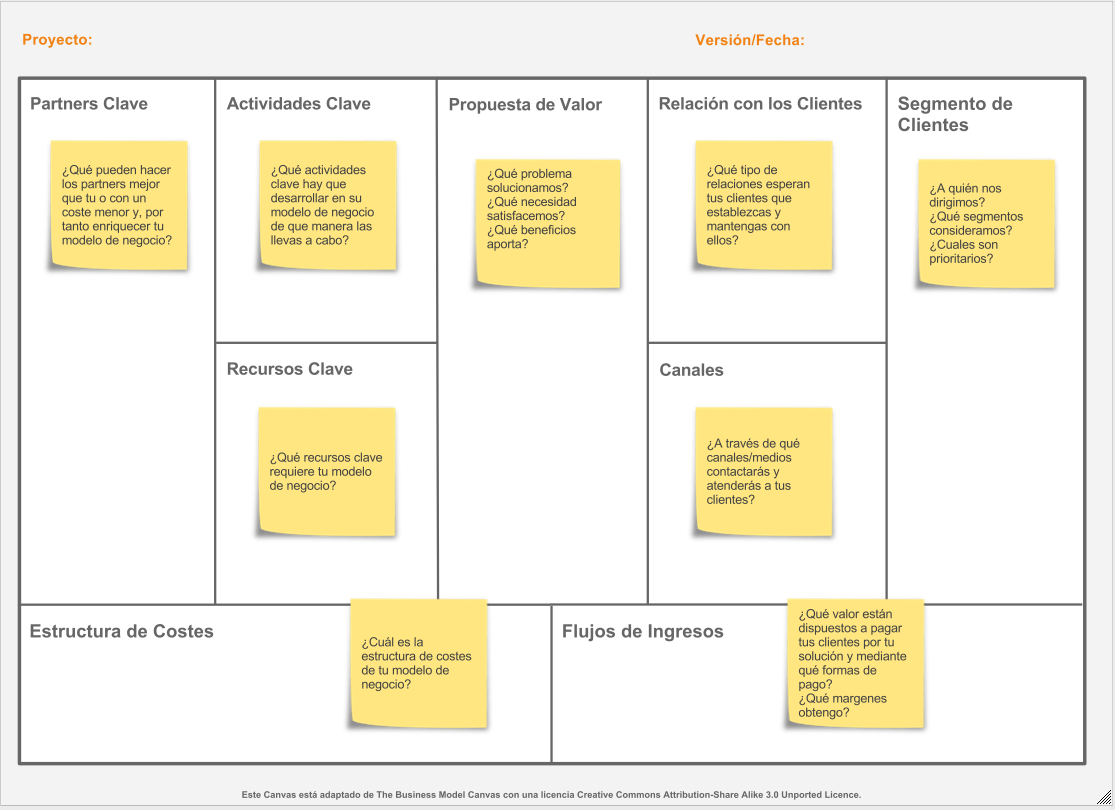
Where can I make a Canvas model?
There are many applications that allow you to create your Canvas model quickly and easily, as they include a default template ready to be completed.
How to fill in the Canvas model? You can use one of the templates below and fill in each field on the computer, or you can print a template and paste posits. This last option is the traditional way to do it, since in a world where business is constantly evolving and changes come very fast, opening the template to change it over and over again may not be very practical. Choose the way that best suits your business, it will not be relevant for the implementation of the template.
Some templates:
- Template of Business Model Canvas de Marcelo Pizarro (Google Drive).
- Business Model Canvas Manager.
- BMC Business Model Canvas.
The 9 elements of the Canvas model
Let’s see how to apply the Canvas model step by step. It is simply a matter of understanding each of the 9 aspects of this tool and gradually completing each one of them. I recommend that you start with your value proposition and then continue with the rest.
1. Value proposition
Esta es tu ventaja competitiva, tu propuesta única de valor o USP (Unique Selling Proposition). Es lo que te diferencia de tus competidores. Y ojo, es por lo que tu cliente está dispuesto a pagar, a comprar tu producto o servicio. Estas son algunas características que pueden incluir tu propuesta de valor:
This is your competitive advantage, your Unique Selling Proposition (USP). It is what differentiates you from your competitors. And watch out, it’s what your customer is willing to pay for, to buy your product or service. These are some characteristics that your value proposition can include:
- To have a novel product or service.
- Improve the performance of an existing product or service.
- To be personalized or customized.
- Design.
2. Market segments
Aquí tendrás que definir quiénes son tus clientes. Los grupos de personas que deseas alcanzar con tu propuesta de valor. Para determinas estos segmentos, primero deberás pensar en cuáles son sus necesidades específicas.
Here you will have to define who your customers are. The groups of people you want to reach with your value proposition. To determine these segments, you must first think about what their specific needs are.
What can your market be like? Some examples are:
- Mass market.
- Niche market.
- Segmented market.
- Diversified market.
3. Channels
Channels refer to how you can reach your target market or audience (the one you have previously defined). How are you going to deliver your value proposition to them? How can your customers buy your products?
Channel types
- Direct
- Indirect
- Own
- From partners
Phases in the channels
- Publicize your products and services.
- Help your customers evaluate your value proposition or competitive advantage.
- Enable your customers to buy your products and services.
- Deliver competitive advantage to your customers.
- Offer after-sales services.
4. Customer relations
What feeling do you want to produce in the customer with your brand? How are you going to connect your value proposition with your customer? What kind of relationship will you establish with your customers?
There are several categories of relationships when creating your business model:
- Personal Assistance
- Exclusive personal assistance
- Self-service
- Automatic services
- Communities
- Collective creation
5. Source of income
How do I generate revenue? How much are my customers willing to pay? How much money does each of my segments generate for me?
On the one hand, we have the revenue sources that will be different in each business model (from the traditional sale of products or services to a subscription fee, rentals…). On the other hand, we have to think about the pricing mechanism for each revenue source. We can opt for fixed prices or dynamic prices (they change according to the market)
If you offer a service in your business and you don’t know how to price it, you can consult our post Tips for pricing a service.
Note: It is very important to always remember that your project must be profitable.
6. Key resources
How are you going to make your value proposition? What resources are you going to use? Are you going to ally with strategic partners to obtain some of these resources?
- Physical resources: premises, vehicles, offices, land…
- Intellectual: patents, copyrights, trademarks…
- Human: the people who are part of your business. Here you can have, for example, an in-house or outsourced sales team.
- Financial: economic resources without counting the initial or social capital.
7. Key Activities
What do you need to implement your value proposition? What actions do you need to take to make the business model work?
Now it is time to think about how we are going to bring all the above elements together. What strategic activities to develop in order to offer the value proposition, take it to customers (reach markets), establish customer relationships and obtain revenues.
Relaciones comerciales, producción, marketing, distribución, mantenimiento…
8. Key partners
What will be your network of suppliers and strategic partners to move your business model forward? These are:
- Investors
- Suppliers
- Business alliances with non-competing companies
- Joint Ventures (a partnership option with another company or companies to create a new business)
- Coopetition (strategic partnership with competing companies)
Benefits you can obtain by establishing strategic partnerships:
- Risk and uncertainty reduction.
- Purchase of resources and activities.
- Optimization and economy of scales.
9. Cost structure
What costs are associated with the implementation of the model?
It is necessary to differentiate between:
Cause of cost
- Cost-driven model: the ultimate goal is to obtain the highest possible profits. To do this, you will need to identify where you can cut costs.
- Value-driven model: this occurs when your business has premium services associated with it (so sometimes less attention is paid to expenses).
Cost characteristics
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Economies of scale (the greater the quantity produced, the greater the savings).
- Economies of scope (it is not only a matter of reducing the average cost per unit produced, but also of optimizing resources with the joint production of several products).
In summary, we can say that the Canvas model is a practical tool with which you can design your business model quickly and modify it as many times as you want when changes occur in your business environment. Take your time to complete each of the elements, paying close attention to the questions posed, and get your project underway.